White Croaker
Genyonemus lineatus
The Science
The Science
Musical fish: the white croaker gets its name from the repetitive croaking noise it makes by rasping a muscle against its swim bladder! [6]
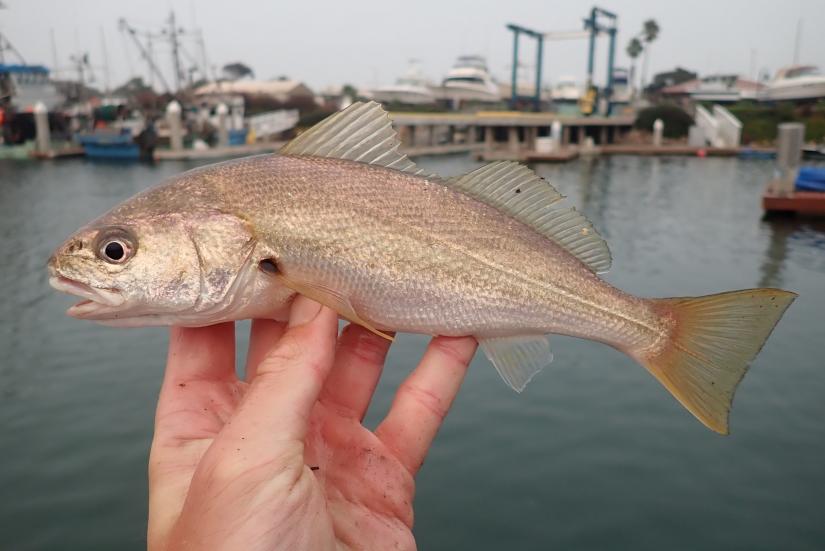

Taxonomic description
- Is the largest species of croaker (family: Sciaenidae).
- White seabass emits croaking sounds by hitting the abdominal muscle against the swim bladder. [2]
- Is a large, mobile fish with an average size of 9 kg (20 lbs) and just over 1 m (3 ft), but the largest recorded white seabass in California was 42 kg (93 lbs) and 1.5 m (5 ft) long. [1,2]
- Blue to gray in color on the back, with a silver belly; and has dark vertical stripes on its back as a juvenile.
Distribution
- Ranges from Magdalena Bay, Baja California, Mexico to the San Francisco area, and in the northern Gulf of California. [1,2]
- During the strong El Niño of 1957-1959 (i.e., warm waters), it was found as far north as Juneau, Alaska. [2]
- Center of the population seems to be off central Baja California. [2]
Life history
- Spawning usually occurs from March to September with a peak in late spring -- early summer. [1]
- Broadcast spawners: it releases gametes in the water for fertilization. Release is usually at night to reduce predation on the eggs, which are the largest (1.3 mm or 0.5” diameter) of any croaker on the west coast. [1,2]
- The age of maturity is uncertain, but all have probably spawned at least once by age 6 (81 cm or 32’ long) and can live to 20 years. [2]
Habitat
- When newly hatched, the seabass inhabits open, shallow coastal waters (4-8 m or 12-30 ft deep), sometimes hanging out in drifting seaweed.
- Juveniles (ages 1-3 yr) may move into protected bays where they use eelgrass beds for cover and feeding grounds; older juveniles are found near piers and jetties with kelp beds nearby.
- Adults use many habitats: rocky reefs, kelp beds, offshore banks or the open ocean. [1]
- Can be found travelling in schools or as a solitary individual. [1]
- Adults prey on Pacific mackerel, Pacific anchovies, Pacific herring, Pacific sardines, market squid and pelagic red crabs. [1,2]
- There are few predators of the white seabass, but they include other fish, sharks, sea lions, and humans. [1]
- A mix of human activities (pollution, overfishing and habitat destruction) and natural environmental conditions contributed to the long term decline of this species but spawning in captivity and release of seabass has enhanced populations. [1,5]
The Fishery
The Fishery
This fish is typically caught off piers, but it is often not recommended to keep because it can accumulate toxins in its body from pollutants! Always check local signs and regulations before keeping white croaker. [3]

Seasonal availability
- Available year-round. [1]
Regulatory and managing authority
- As established by the Marine Life Management Act, the California Fish and Game Commission regulates the fishery, and the California Department of Fish and Wildlife manages this fishery. [13]
- The white croaker population is monitored by the Office of Environmental Health Hazard Assessment due to concerns over pollution accumulation in this fish. [3]
Gear type
- Typically caught using hook and line, but is also caught as bycatch by fisheries using entagling nets, surrounding nets, trawl nets, set longline, and hook and line. [3]
Status of the fishery
- Little information is known about the white croaker population, but a decrease in landings have led to some concern that this species is decreasing in population. [3]
- The white croaker fishery is primarily recreational. [14]
Potential ecosystem impacts
- Lost gear from hook and line fishing creates marine debris when fishing line is lost, and can entangle other wildlife. [3]
The Seafood
The Seafood
California piers will often have signs denoting if white croaker from the area is safe to eat or not. [9]
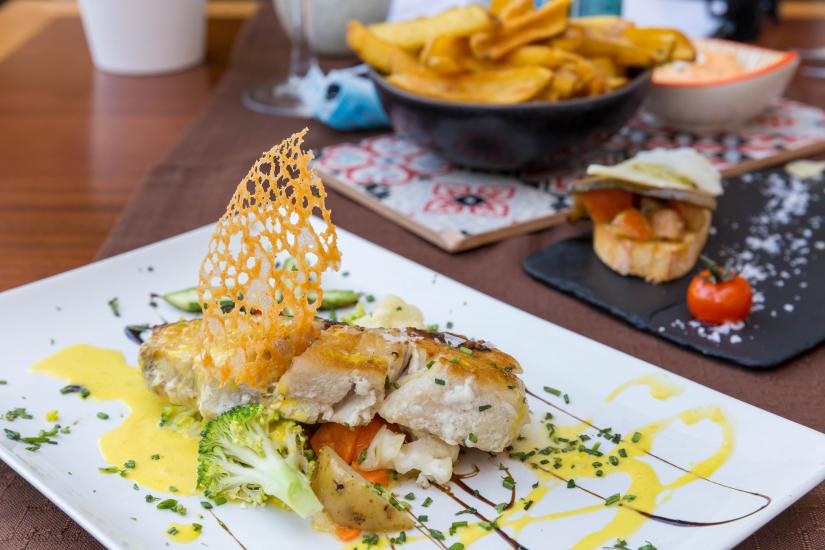

Edible portions
- The whole fish is edible. [8]
Description of meat
- The meat is mild-flavored and is safe to consume depending on where it is caught. [1,9]
Culinary uses
-
For a recipe for pan-fried croaker, visit The Spruce Eats. [8]
-
For a barbequed croaker recipe, visit Dobby's Signature. [15]
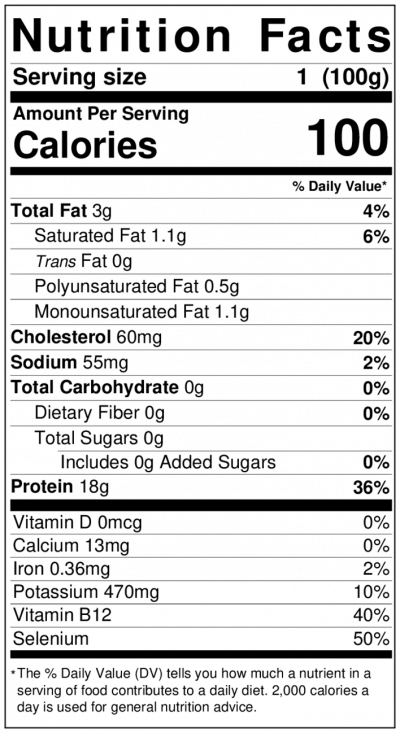
Nutritional information
- Nutritional information on 100g of raw Atlantic croaker (Micropogonias undulatus) can be found on the table to the right. [7]
Toxicity report
- Because this fish sometimes congregates around sewer outfalls, it can accumulate toxins that make it unsafe for human consumption. Refer to local guidelines to see if it is safe to eat this fish. [1,9]
Seasonal availability
- This fish is available year-round. [1]
References
[1] Jones, K. 2018. Pier Fishing in California. Web. https://www.pierfishing.com/white-croaker/. Accessed 10 July 2020.
[2] California Department of Fish and Wildlife. 2013. California Marine Sportfish Identification: Croakers. Web. https://wildlife.ca.gov/Fishing/Ocean/Fish-ID/Sportfish/Croakers. Accessed 10 July 2020.
[3] Ocean Protection Council. n.d. Fishery-at-a-Glance: White Croaker. Web. http://www.opc.ca.gov/webmaster/_media_library/2019/08/Draft_Marine-Spe…. Accessed 10 July 2020.
[4] Love, M.S., et al. 1984. Fishery Bulletin 82(1). Web. https://www.st.nmfs.noaa.gov/spo/FishBull/82-1/love.pdf. Accessed 10 July 2020.
[5] Snow, J. Mexico-Fish, Birds, Crabs, Marine Life, Shells and Terrestrial Life. n.d. White Croaker. Web. http://mexican-fish.com/white-croaker/. Accessed 10 July 2020.
[6] Fishbase. n.d. Family Sciaenidae-Drums or croakers. Web. https://www.fishbase.se/Summary/FamilySummary.php?Family=Sciaenidae. Accessed 10 July 2020.
[7] Self. n.d. Fish, croaker, Atlantic, raw. NutritionData. Web. https://nutritiondata.self.com/facts/finfish-and-shellfish-products/404…. Accessed 20 July 2020.
[8] Imatome-Yun, N. 2019. Korean Fried Whole Fish. The Spruce Eats. Web. https://www.thespruceeats.com/korean-yellow-croaker-2118566. Accessed 22 July 2020.
[9] California Office of Environmental Health Hazard Assessment. 2018. A Guide to Eating Fish from the California Coast Advisory for Areas Without Site-Specific Advice. Web. https://oehha.ca.gov/media/downloads/advisories/coastalposter092718.pdf. Accessed 22 July 2020.
[10] Cantrell, B. iNaturalist. 2020. Digital image. Web. https://www.inaturalist.org/photos/95574730. Accessed 26 February 2021.
[11] lizardman69. iNaturalist. 2020. Digital image. Web. https://www.inaturalist.org/photos/104431165. Accessed 26 February 2021.
[12] Verch, M. flickr. 2020. Wild croaker fillet (white fish) on the grill served with flaked salt at restaurant Q11 in Pollença, Majorca. Digital image. Web. https://flickr.com/photos/160866001@N07/50165895562. Accessed 26 February 2021.
[13] Marine Life Management Act. n.d. California Department of Fish and Wildlife. Web. https://wildlife.ca.gov/Conservation/Marine/MLMA. Accessed 24 August 2020.
[14] California Department of Fish and Wildlife. 2019. White Croaker, Genyonemus lineatus, Enhanced Status Report. Web. https://marinespecies.wildlife.ca.gov/white-croaker/. Accessed 14 December 2020.
[15] Dobby's Signature. 2013. Barbecued Marinated Croaker Fish Recipe on Street Foodie Waka. Web. https://dobbyssignature.com/barbecued-marinated-croaker-fish-recipe-on-…. Accessed 4 February 2021.
[16] Schwarz, C. iNaturalist. 2018. Digital image. Web. https://www.inaturalist.org/photos/23247287. Accessed 26 February 2021.