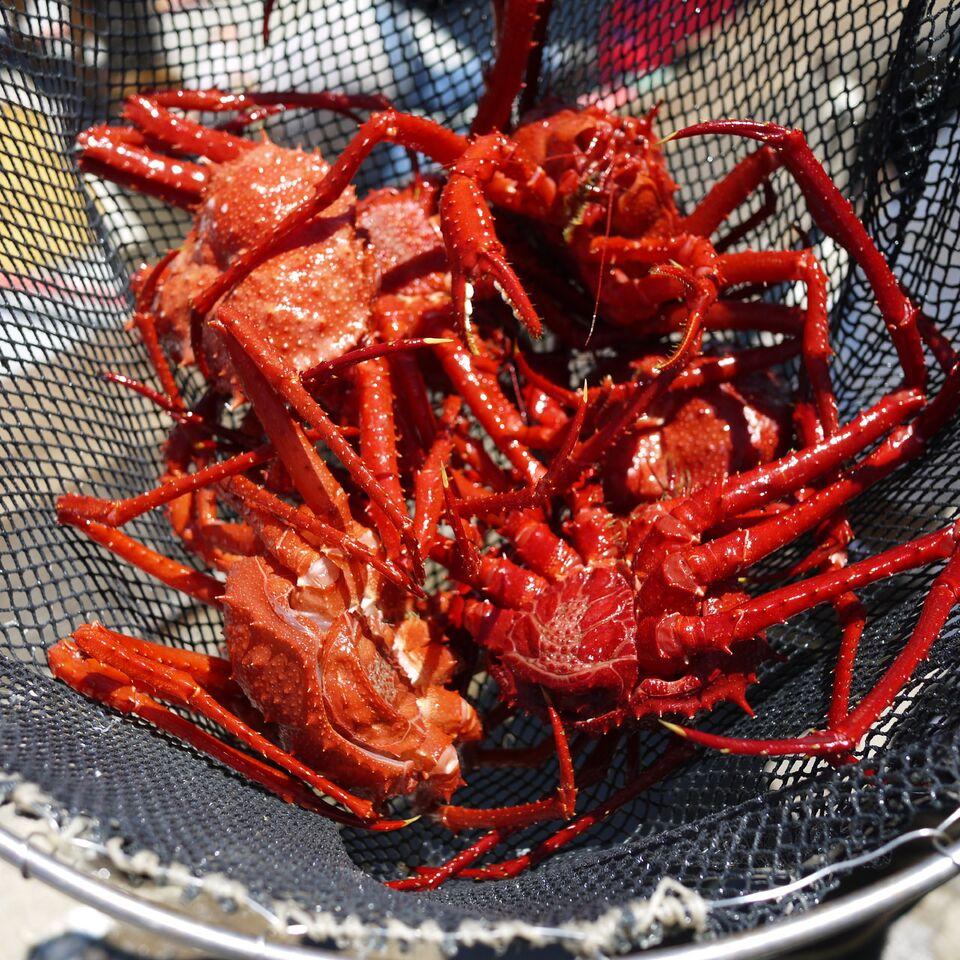
Scarlet King Crab
Lithodes couesi
The Science
THE SCIENCE
Scarlet King Crab forms pods, piles of 1000s of individuals that can be several feet high, this behavior is thought to be defense against predators.

Taxonomic description
- Amongst king crab species, the scarlett king crab is comparatively smaller. [6]
- Has a bright red, or scarlet, carapace.
- Ranges from 3.6-9.07 kg (8-20 lbs) in weight. [15]
Distribution
- Found from the Bering Sea, Gulf of Alaska, southward along the eastern Pacific slope to San Diego. [4]
Life history
- Although not much is known about the scarlet king crab, other king crab species can survive 20 to 30 years in the wild and reach sexual maturity at 4 to 5 years old. [2]
- For the similar species Paralithodes camtschatica (also known as Alaskan king crab), mating occurs once a year during spring immediately or soon after the female has molted. [5]
- Females of the species Paralithodes camtschatica carry eggs under their broad abdomen for 12 months, after which small larvae emerge from the eggs. [5]
Habitat
- Found in depths from intertidal to 183 meters (600 ft). [14]
- The species Paralithodes camtschatica mainly feeds on mollusks and echinoderms. [1]
- Preyed on by the shortspine thornyhead. [14]
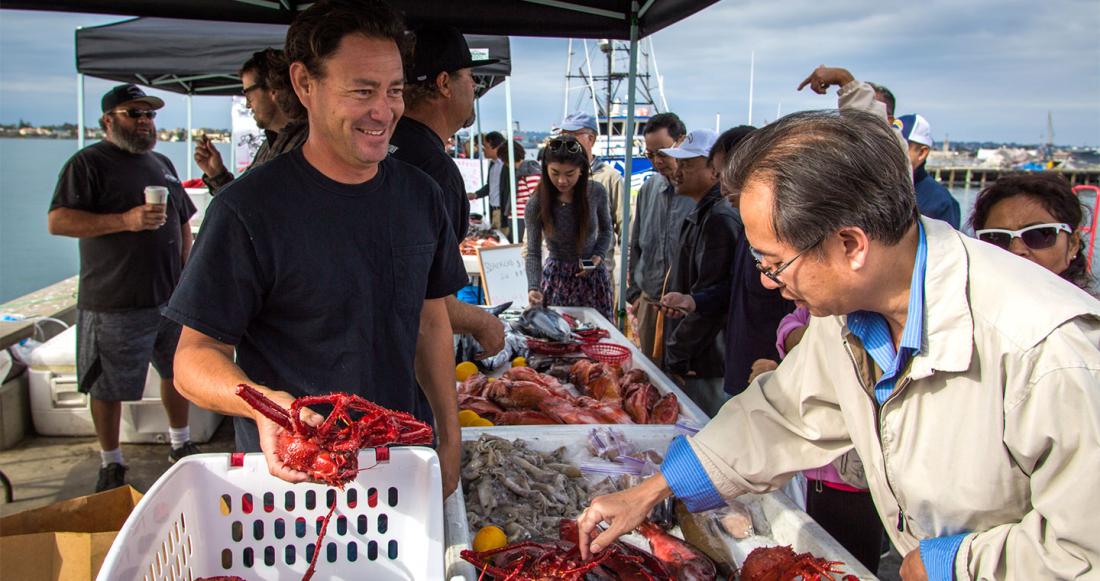
The Fishery
THE FISHERY
Traps and bottom trawls negatively impact the ocean floor as they are dragged by the ships that carry them.

Seasonal availability
- Available year round.
Regulatory and managing authority
- As established by the Marine Life Management Act, the California Fish and Game Commission (CFGC) regulates the fishery, and the California Department of Fish and Wildlife (CDFW) manages this fishery in state waters. [7,8]
Gear type
- Several trap designs are used in the rock crab fishery. The most popular is a single chamber, rectangular trap of two-by-four- or two-by-two-in. welded wire mesh. [10]
Status of the fishery
- No fishery is designated specifically for this species, so little to no information on stock sizes, recruitment rates, effects of oceanographic regimes on this species. [11]
- There are no conservation concerns known for this species, but fishing pressure and global warming are thought to have reduced the population size of the related Alaskan king crab. [9]
Potential ecosystem impacts
- There may be issues of habitat damange and ghost fishing from lost traps.
- Specific information about this fishery is not known, but most crab traps are designed for release of immature crabs to avoid catching individuals before they are able to reproduce. [11]
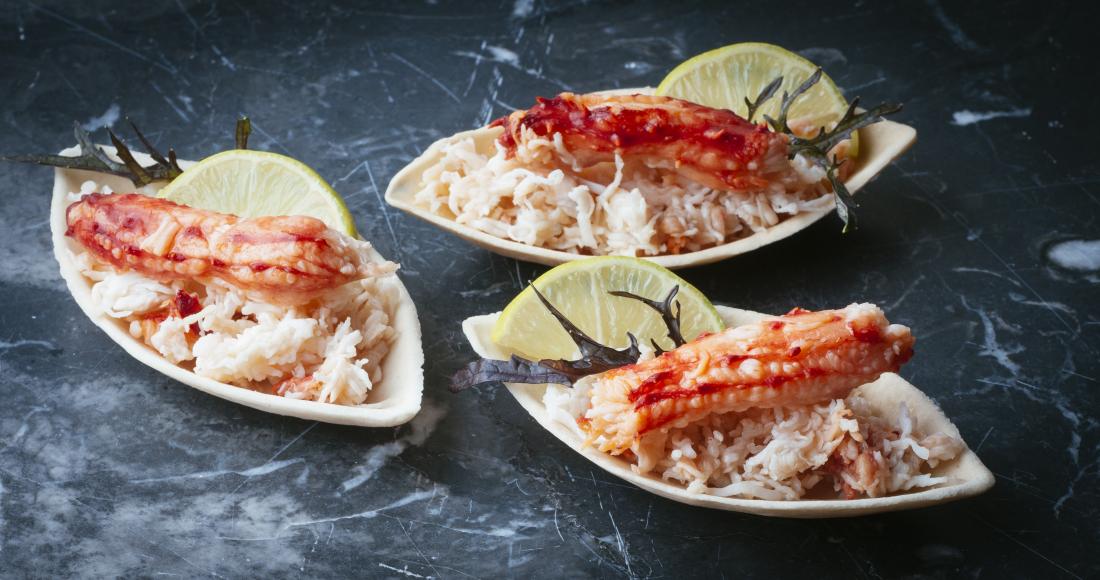
The Seafood
THE SEAFOOD
Domoic acid, a product of harmful algal blooms, can be found in the viscera (guts) of certain crabs during blooms.

Edible portions
- Legs, muscle (meat) inside body walls; whole body may be used in broth and soup. [1]
- One of the highest meat-to-shell ratios, 3 pounds of whole crab yield around 2 pounds of meat. [18]
Description of meat
- Meat is soft, flaky, white, delicate, and sweet-tasting.
Culinary uses
- Available live; Cooking instructions at reference. [12]
- Most often served by itself with a side of butter; can be used in pasta, crab-cake, sushi, etc.
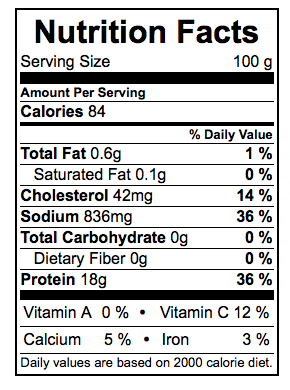
Nutritional information
- Nutritional information for 100g of raw Alaskan king crab (Paralithodes camtschatica) is displayed. [13]
Toxicity report
- Although domoic acid, a naturally occuring toxin, is sometimes found in shellfish that occur in shallower waters [3]; this species is generally caught in deeper waters reducing risk of exposure to blooms.
- Avoid eating the viscera, where toxins can be concentrated.
Seasonal availability
- Available year round.
References
[1] Alaska Sealife Center. 2017. Red King Crab. Web. http://www.alaskasealife.org/aslc_resident_species/46. Accessed 30 May 2017.
[2] Kato, S., W. Lee, S. Salapare. Guide to underutilized species of California. 83rd ed. Vol. 01. Tiburon: Tiburon Laboratory, 1983. Print.
[3] Shuman, C.. Health Advisories and Closures for California Finfish, Shellfish and Crustaceans. Health Advisories and Closures for California Finfish, Shellfish and Crustaceans. California Department of Fish and Wildlife, 16 May 2017. Web. https://www.wildlife.ca.gov/Fishing/Ocean/Health-Advisories. Accessed 30 May 2017.
[4] Encyclopedia of Life. n.d. Deep Sea Crab. Web. https://eol.org/pages/46505285. Accessed 11 Sept 2020.
[5] Luchsinger, S.. "Reproduction and Lifecycle." Red King Crab. Jackson and Tull, 27 Apr. 2007. Web. http://bioweb.uwlax.edu/bio203/s2007/luchsing_sara/reproduction_and_lifecyle.htm. Accessed 09 May 2017.
[6] "Alaskan Seafood." Alaskan King Crab Co. — All About King Crab. Trust E Certified Privacy, 2011. Web. https://www.alaskankingcrab.com/pages/king-crab. Accessed 30 May 2017.
[7] Marine Life Management Act. n.d. California Department of Fish and Wildlife. Web. https://wildlife.ca.gov/Conservation/Marine/MLMA. Accessed 24 August 2020.
[8] Shuman, Craig, Dr. "Data-Poor Fisheries Management." California Department of Fish and Wildlife. CDFW, 2010. Web. https://www.wildlife.ca.gov/Conservation/Marine/Data-Poor-Fisheries. Accessed 30 May 2017.
[9] Alaska Department of Fish and Game. Commercial Fisheries. 2017. Web. http://www.adfg.alaska.gov/index.cfm?adfg=fishingCommercial.main. Accessed 30 May 2017.
[10] California Department of Fish and Game. "Rock Crabs." Annual Status of the Fisheries Report. California Department of Fish and Game, Dec. 2001. Web. https://nrm.dfg.ca.gov/FileHandler.ashx?DocumentID=34395&inline. Accessed 30 May 2017.
[11] California Department of Fish and Game. "Rock Crabs: History of the Fisheries." California’s Living Marine Resources: A Status Report. California Department of Fish and Game, Dec. 2001. Web. https://nrm.dfg.ca.gov/FileHandler.ashx?DocumentID=34335&inline. Accessed 30 May 2017.
[12] Stradley, Linda. "How to Cook Perfect King Crab Legs, Whats Cooking America." What's Cooking America. N.p., 19 May 2017. Web. https://whatscookingamerica.net/Q-A/KingCrab.htm. Accessed 30 May 2017.
[13] Crustaceans, raw, alaska king, crab. Nutritionvalue.org. Web. https://www.nutritionvalue.org/Crustaceans%2C_raw%2C_alaska_king%2C_crab_nutritional_value.html. Accessed 21 September 2017.
[14] Encyclopedia of Life. n.d. Deep Sea Crab. Web. https://eol.org/pages/46505285. Accessed 11 Sept 2020.
[15] National Oceanic and Atmospheric Association. n.d. Deep Coral Communities. Web. https://nmssanctuaries.blob.core.windows.net/sanctuaries-prod/media/archive/education/teachers/deep-coral-communities/deep-sea-poster-with-id-guide.pdf. Accessed 11 Sept 2020.
[16] Houston, J. California Sea Grant. 2015. Fisheries in San Diego, CA. Digital image. Web. https://flickr.com/photos/caseagrant/38976733312. Accessed 24 February 2021.
[17] MARCELODLT. Shutterstock. n.d. Elegant and delicious morsel of crab and ground for cocktail. Digital image. Web. https://www.shutterstock.com/image-photo/elegant-delicious-morsel-crab-…. Accessed 24 February 2021.
[18] Crabbing Hub. Web. https://crabbinghub.com/which-crab-has-the-most-meat-a-quick-comparison/. Accessed 4 January 2022.