Pacific Bonito
Sarda lineolata
The Science
THE SCIENCE
Bonito populations fluctuate in accordance with the warm/cold water periods associated with the Pacific Decadal Oscillation.
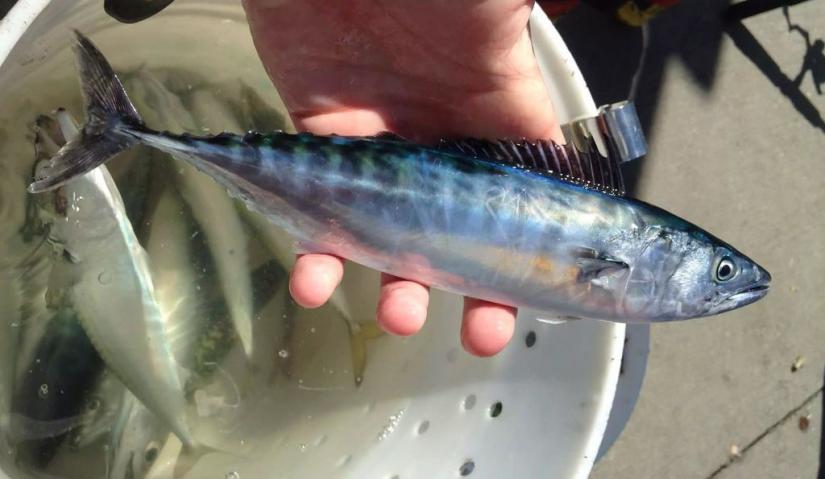

Taxonomic description
- Head is pointed and conical with a large mouth.
- Has a compressed body with slanted dark stripes on their backs and upper sides.
- Lower jaw has 14-25 teeth, and is moderately large.
- Reaches 79-102 cm (31-40 in) in length and can weigh up to 11 kg (24 pounds). [4]
- Characterized by a large spleen and lack of swim bladder. [7]
- Was formerly considered subspecies of Sarda chiliensis. [18]
Distribution
- Ranges from the Pacific Ocean from the coast of Alaska all the way down to the tip of Baja California, Mexico. [9]
Life history
- Reaches sexual maturity at the age of 2 and have a maximum lifespan of 6 years. [2]
- Spawning generally occurs from late January until May. [11]
Habitat
- Bonito is a pelagic fish that lives 80-200 meters (262-328 ft.) deep, migrating farther offshore as it grows older.
- Eats fish (such as sardines and anchovies) as well as squid. [3]
- Predators of bonito are larger fish such as tuna, bonito also prey on each other as well. [1]
The Fishery
THE FISHERY
Fishing for bonito occurs offshore in 300-600 feet of water.
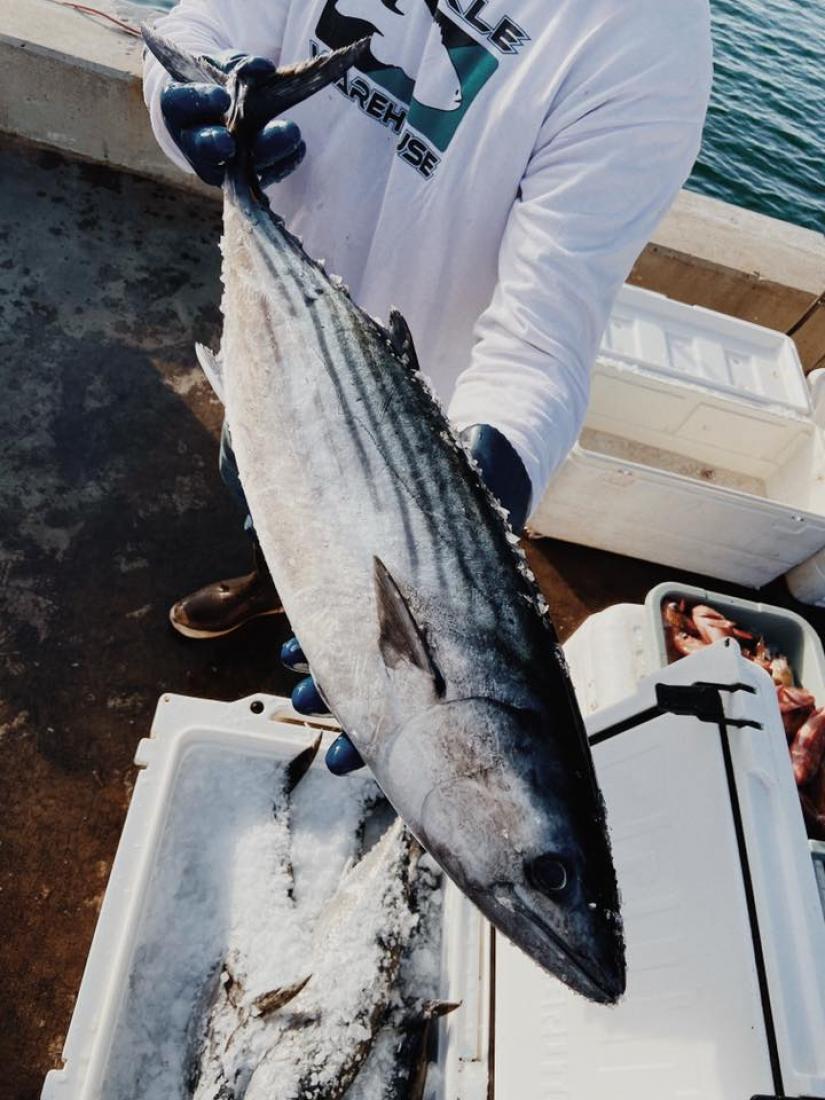

Seasonal availability
- Fishing is allowed year-round, but most catch is landed from June-November. [3]
Regulatory and managing authority
- As established by the Marine Life Management Act, the California Department of Fish and Wildlife (CDFW) collects data on and manages this fishery. [2,15]
Gear type
- Mostly taken by purse seine, but are also caught by gill nets, trawl, and hook and line. [2,8]
Status of the fishery
- Currently, bonito is placed in the category of least concern because the catch per year has decreased significantly since the 1990s due to increased regulation and decreased market demand.
- Catch peaked in 1966 with 4.6 million fish declining with a loss of 659,000 in the 1990s. [3]
- In 2014, 70,982 pounds (32,196 kg.) of Pacific Bonito were caught in California. [6]
Potential ecosystem impacts
- Purse seines are non-selective, which poses risks to non-target species. [12]
The Seafood
THE SEAFOOD
Bonito is sometimes dried, fermented, and smoked to make bonito flakes, or Katsuobushi, in Japanese cuisin
Edible portions
- Can be eaten whole. [4]
Description of meat
- Meat is deep red to pink, soft with a fishy smell but a bold and flavorful taste. [14]
Culinary uses
- Available whole, as filets, or steaks.
- Should be bled and put on ice immediately after catching, and bloodlines should be removed. [14]
- Generally brined prior to cooking. [5]
- For a Japanese simmered bonito recipe, visit Recipe Tin Japan. [16]
- For recipe for grilled bonito, visit Greedy Gourmet. [17]
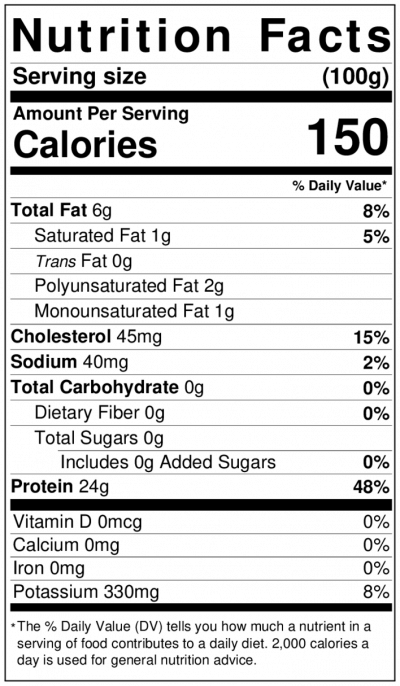
Nutritional information
- For fresh Bonito, there are 5 calories per 129 serving (100 g) and 28 grams of protein. [13]
Toxicity report
- As with other top predators, may contain high mercury levels; follow consumer guidelines especially for pregnant women and children. [10]
Seasonal availability
- Available year round.
References
[1] Massachusetts Department of Energy and Environmental affairs. 2017. Atlantic Bonito. Web. http://www.mass.gov/eea/agencies/dfg/dmf/recreational-fishing/atlantic-bonito.html#food. Date accessed: 27 May 2017.
[2] California Department of Fish and Wildlife. 2019. Pacific Bonito, Sarda chiliensis, Enhanced Status Report. Web. https://marinespecies.wildlife.ca.gov/pacific-bonito/. Accessed 4 September 2020.
[3] Lewis, M. 2008. California Department of Fish and Wildlife. Pacific Bonito, Sarda chiliensis. Status of the Fisheries 2008. Web. https://nrm.dfg.ca.gov/FileHandler.ashx?DocumentID=34441&inline. Accessed 4 September 2020.
[4] CDFW. 2016-2017. "California Marine Sportfish Identification: Tuna & Mackerels." Web. https://www.wildlife.ca.gov/Fishing/Ocean/Fish-ID/Sportfish/Tuna-And-Mackerels#bonito. Accessed: 12 April 2017
[5] Canncel, C.. 2015. How to Cook Bonito Fish."Web. http://www.livestrong.com/article/547462-how-to-cook-bonita-fish/. Accessed: 20 May 2017.
[6] CDFW. 2014. Final Commercial Landings. Web. https://www.wildlife.ca.gov/Fishing/Commercial/Landings#26004609-2014. Accessed: 20 May 2017.
[7] Food and Agricultural Organization of the United Nations. 2017. Sarda Chilensis. Food and Agricultural Organization of the United Nations. Web. http://www.fao.org/fishery/species/3275/en. Accessed: 12 April 2017.
[8] Monterey Bay Aquarium Seafood Watch. 1999-2017. Fishing and Farming Methods. Web. http://www.seafoodwatch.org/ocean-issues/fishing-and-farming-methods. Accessed: 1 May 2017.
[9] Luna, S. 1983. Sarda chiliensis, Eastern Pacific Bonito. Web. http://www.fishbase.org/summary/113. Date Accessed: 21 April 2017
[10] U.S. Food and Drug Administration. 2017. Mercury Levels in Commercial Fish and Shellfish (1990-2012). Web. https://www.fda.gov/food/metals-and-your-food/mercury-levels-commercial-fish-and-shellfish-1990-2012. Accessed 4 September 2020.
[11] NOAA Fisheries. 2014. Purse Seine: Fishing Gear and Risks to Protected Species. Web. http://www.nmfs.noaa.gov/pr/interactions/gear/purseseine.htm. Accessed: 29 April 2017.
[12] Snow, J. Mexico- Fish, Marine Life, Birds and Terrestrial Life. Pacific Bonito. http://www.mexican-fish.com/pacific-bonito/. Accessed: 12 April 2017
[13] Pacific Bonito. Web. Myfitnesspal.com. Accessed: 21 September 2017.
[14] Finn's Fishing Tips. n.d. What does Bonito Fish Taste Like? Web. https://finnsfishingtips.com/bonito-fish-taste/. Accessed 28 Sept 2020.
[15] Marine Life Management Act. n.d. California Department of Fish and Wildlife. Web. https://wildlife.ca.gov/Conservation/Marine/MLMA. Accessed 24 August 2020.
[16] Yukimo. Recipe Tin Japan. 2019. Bonito Kakuni. Web. https://japan.recipetineats.com/bonito-kakuni-simmered-bonito-cubes/. Accessed 19 January 2021.
[17] Minnaar, M. Greedy Gourmet. 2018. Grilled Bonito. Web. https://www.greedygourmet.com/recipes-by-course/main-course/grilled-bon…. Accessed 19 January 2021.
[18] Binohlan, C.B. FishBase. n.d. Sarda lineolata, Pacific Bonito. Web. https://www.fishbase.se/summary/Sarda-lineolata.html. Accessed 18 February 2021.
[19] Armstrong, L. iNaturalist. 2008. Digital image. Web. https://www.inaturalist.org/photos/27291808. Accessed 18 February 2021.
[20] Manning, I. iNaturalist. 2015. Digital image. Web. https://www.inaturalist.org/photos/13414261. Accessed 18 February 2021.
[21] Tuna Harbor Dockside Market. Facebook. 2020. Digital image. Web. https://www.facebook.com/thdocksidemarket/photos/3264148366947757. Accessed 18 February 2021.
[22] jatrax. iStock. 2015. Tuna steak grilled with orange sauce stock photo. Digital image. Web. https://www.istockphoto.com/photo/tuna-steak-grilled-with-orange-sauce-…. Accessed 18 February 2021.